Search

News & Events
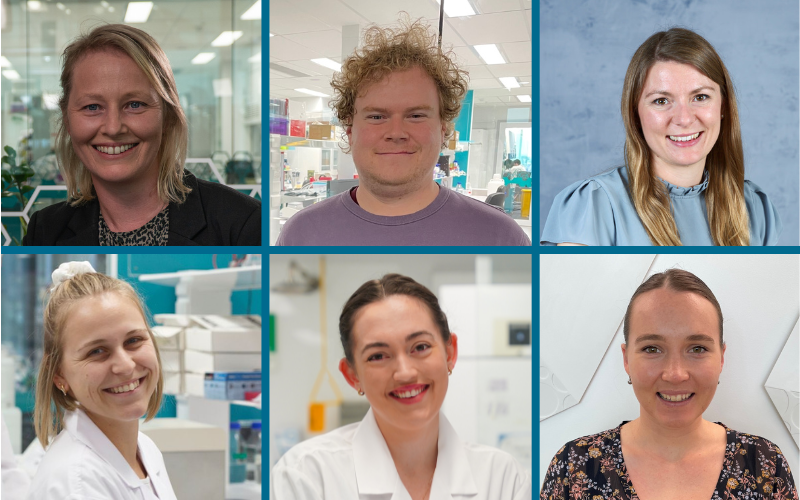
Wal-yan respiratory researchers head to Milan to participate in international congressThe Wal-yan Respiratory Research Centre is proud to have a team of researchers taking part in, and contributing to, the outstanding scientific programme of the European Respiratory Society International Congress, taking place in Milan.
News & Events
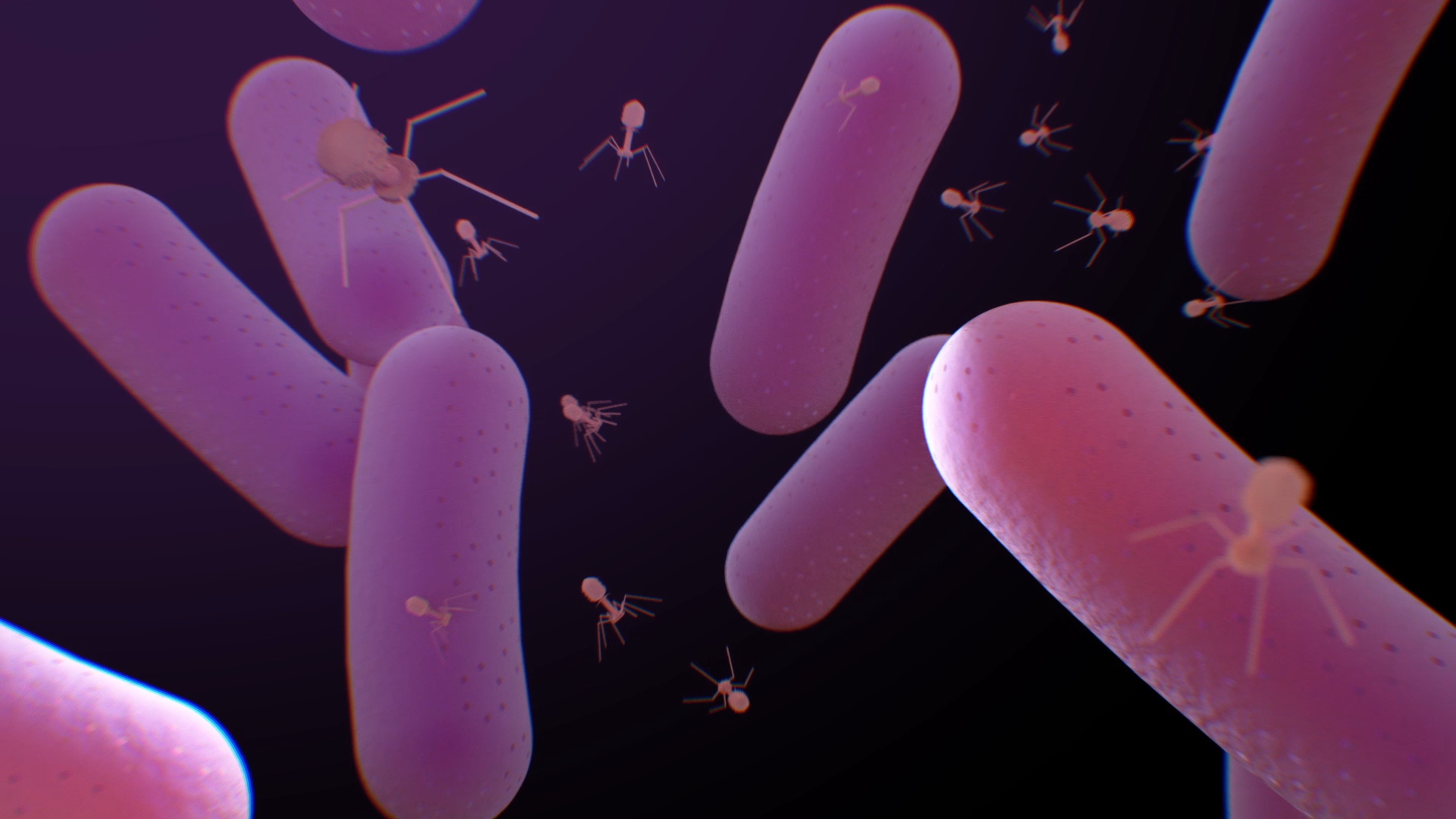
A new phage discovery in the fight against Antimicrobial ResistanceJack Canning, a PhD researcher in the Wal-yan Respiratory Centre’s Phage WA team, has made a significant finding in the search for alternative treatments to antimicrobial-resistant (AMR) bacteria.

News & Events
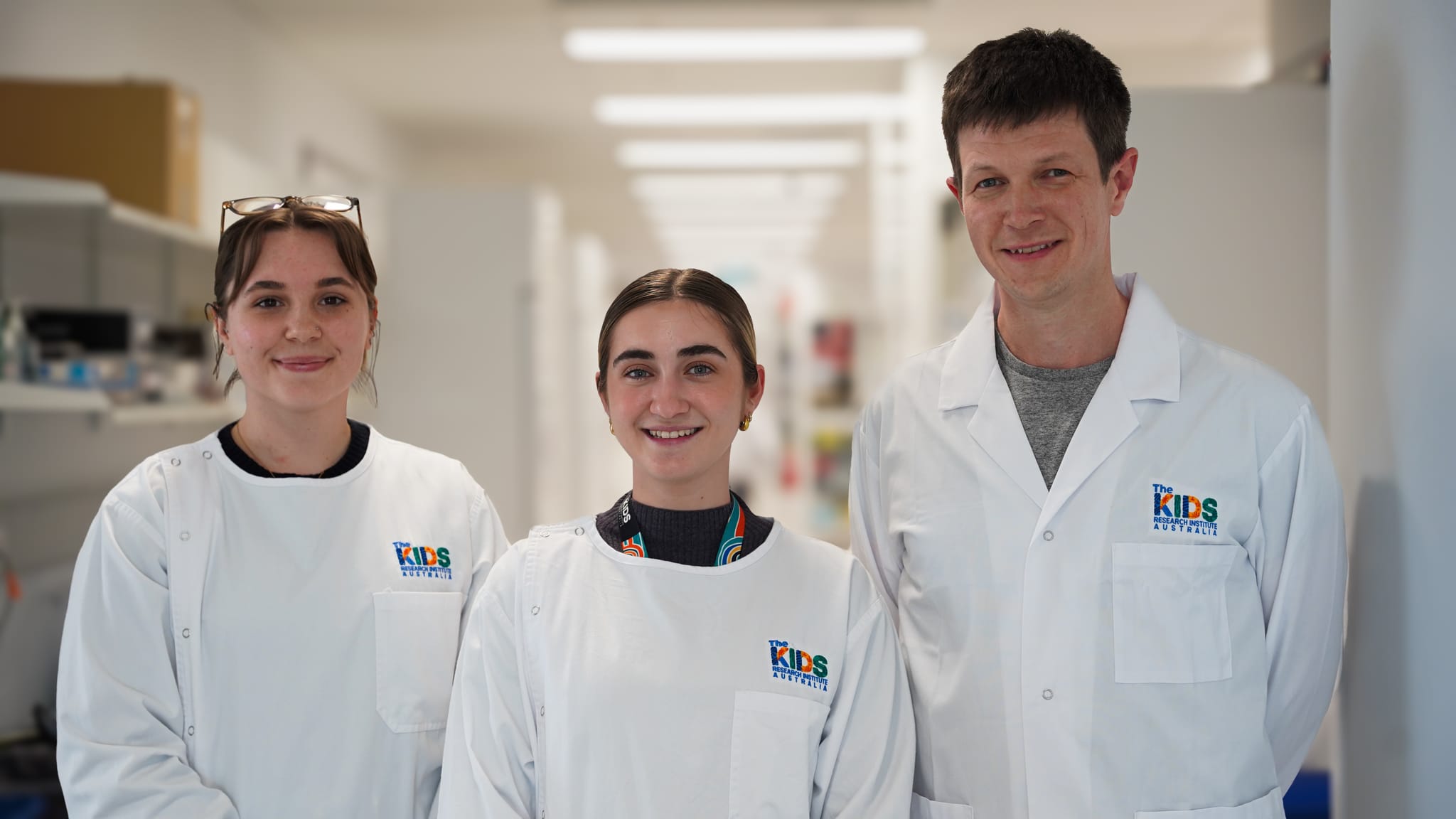
Immune patterns linked to childhood asthma riskNew research digs deeper into how children's immune systems handle viral challenges

As part of our research development and planning we invite members of the community to work with us. Click here to find out how.

News & Events
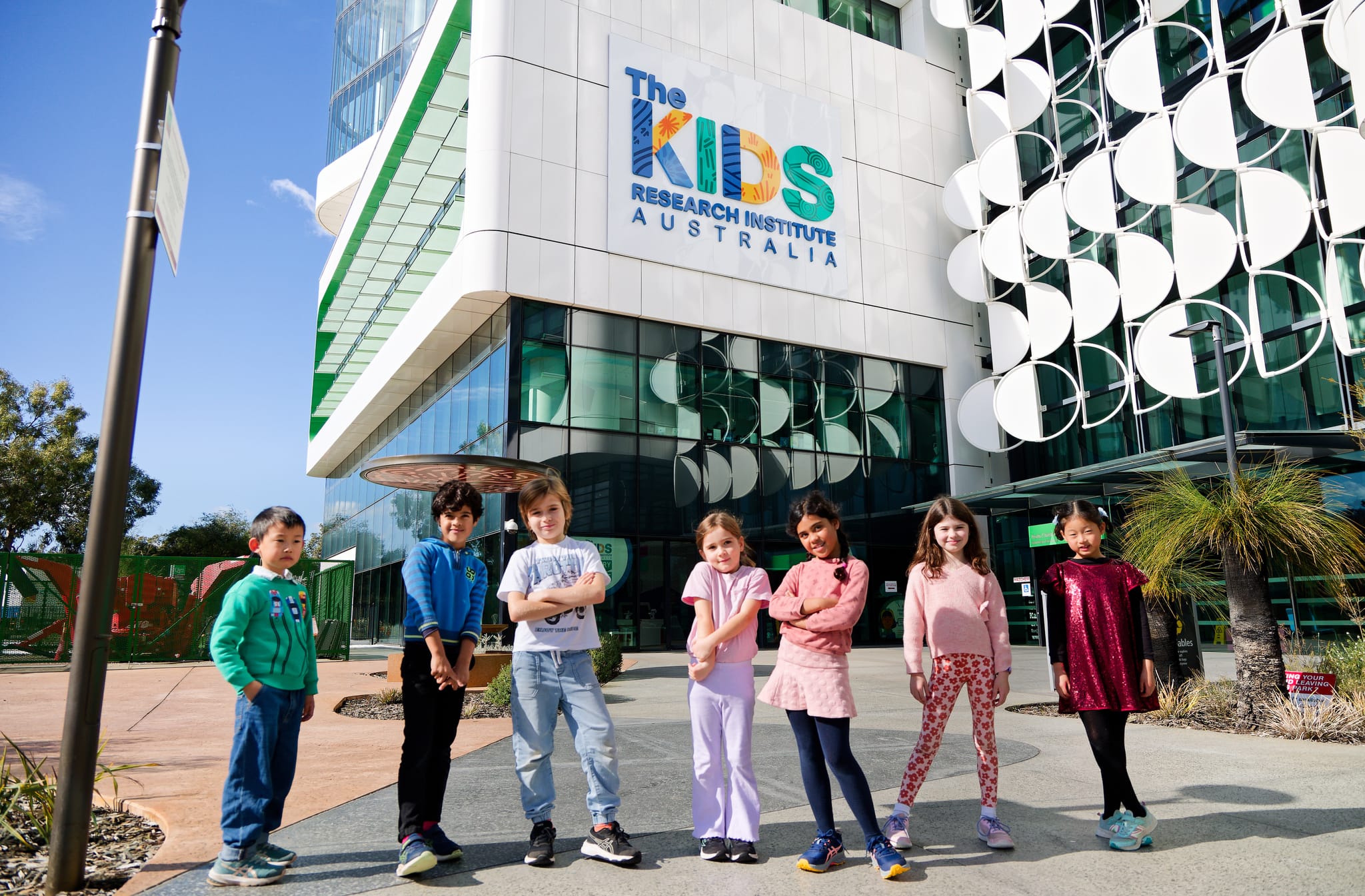
Funding boost for groundbreaking child health researchResearchers from The Kids Research Institute Australia will share in almost $4 million in grants to continue groundbreaking research to tackle childhood cancer, asthma, respiratory viral infections and more.
