Search
News & Events
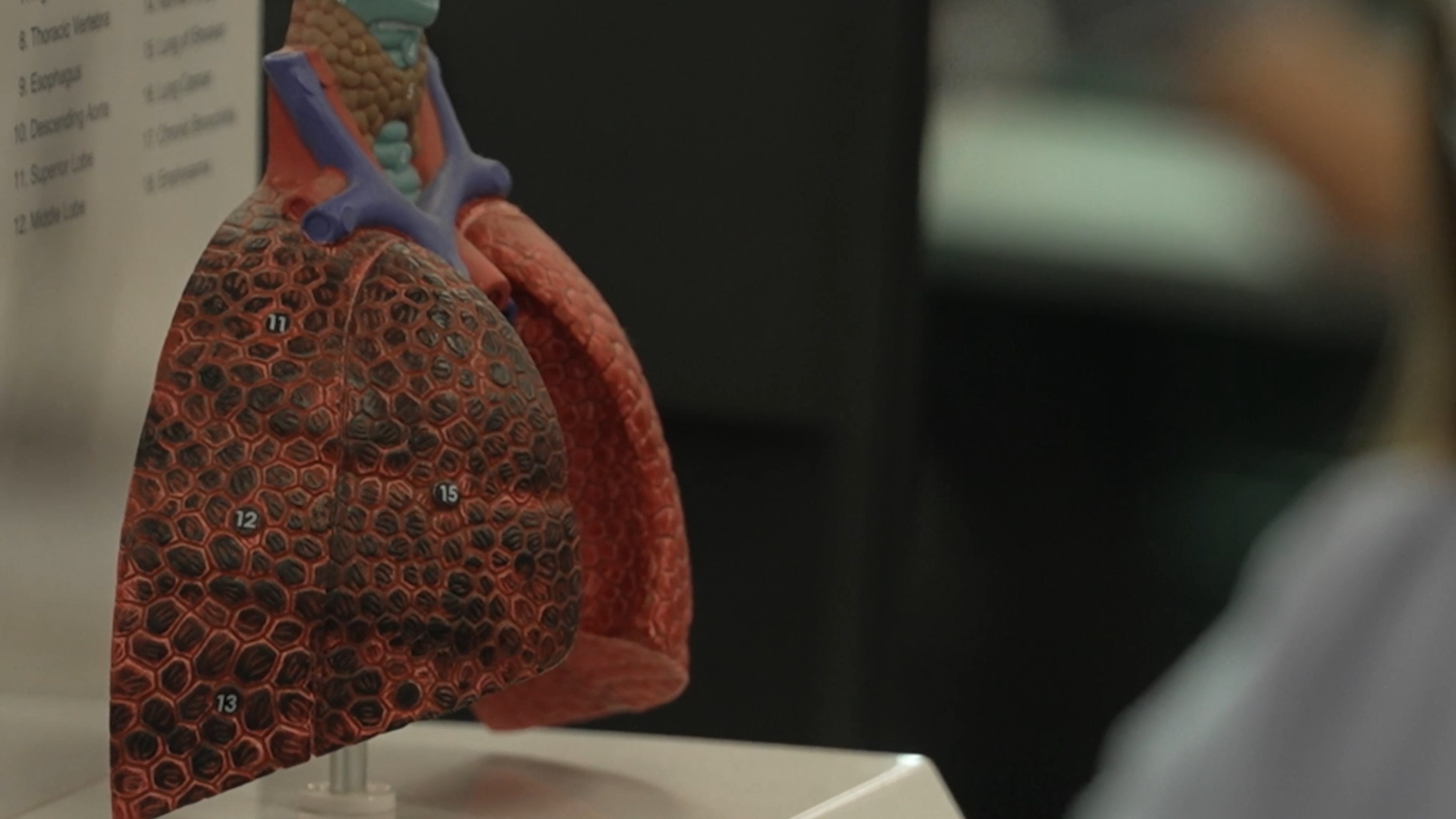
International clinical trial reduced lung inflammation in young kids with cystic fibrosisPromising results from an Australian-led clinical trial could drastically change the way we care for young children with cystic fibrosis (CF).

News & Events
Raine Foundation grants to support key child health researchThree outstanding young researchers from The Kids Research Institute Australia have been named Raine Fellows and received valuable Raine Priming Grants to support their child health research.

News & Events
The Kids researchers named as finalists in 2021 Premier’s Science AwardsFour The Kids Research Institute Australia researchers – working across diverse fields including paediatric anaesthesia, bioinformatics, ear health, and the health impacts of biodiesel exhaust – have been named as finalists in the 2021 Premier’s Science Awards.

News & Events
Four The Kids researchers in running for West Australian of the Year AwardsFour outstanding The Kids Research Institute Australia researchers, including Institute Director, Professor Jonathan Carapetis AM, have been named finalists in the 2021 Western Australian of the Year Awards.

News & Events
Wal-yan researchers secure three MRFF grants to tackle childhood lung diseaseThe Wal-yan Respiratory Research Centre is thrilled to see three researchers awarded prestigious Medical Research Future Fund (MRFF) Chronic Respiratory Conditions grants to improve lung health in children.
