Search
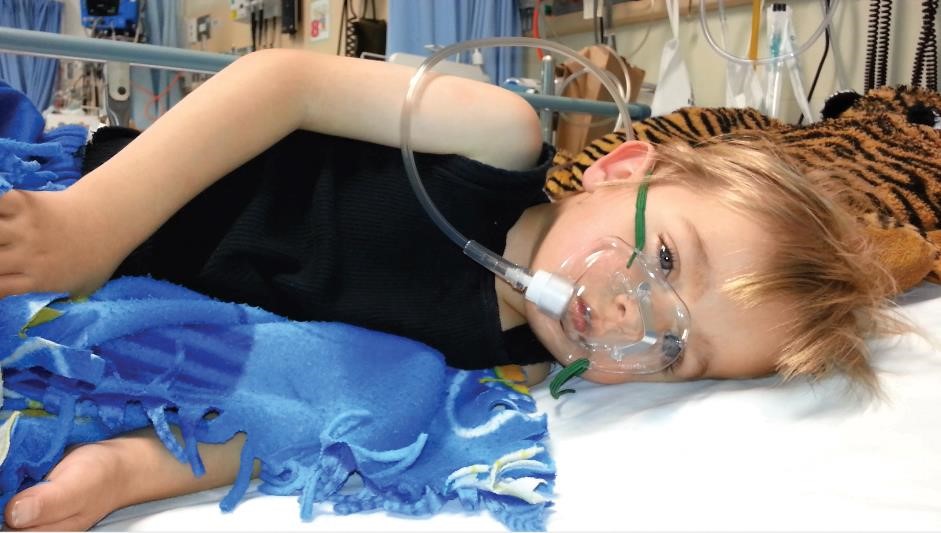
WA researchers lead global centre to eliminate childhood asthma
An ambitious project that could stop children developing asthma is the centrepiece of a new world-class respiratory research centre launched in Perth.
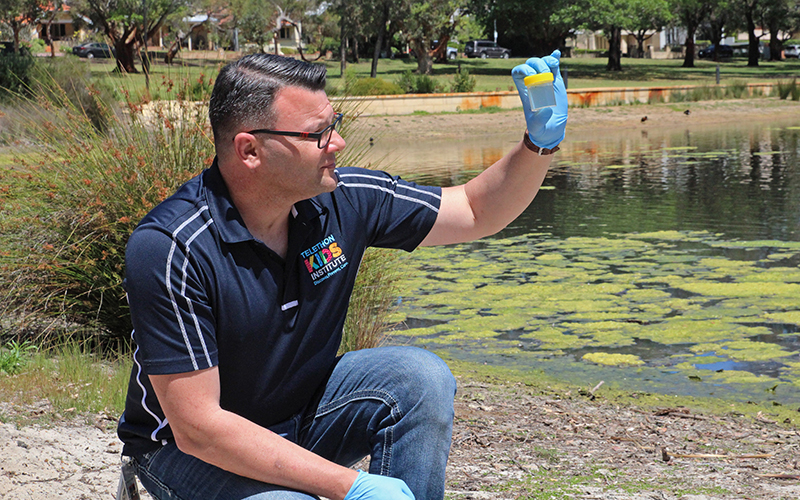

Could Perth lakes hold the secret to fighting antibiotic-resistant superbugs?
Perth researchers have discovered a predatory virus living in the city’s lakes and rivers that can fight antibiotic-resistant superbugs in children.

Pre-term kids get green light to exercise
Parents of children born prematurely have expressed concerns about their child’s lung health when they exercise, with symptoms such as breathlessness.
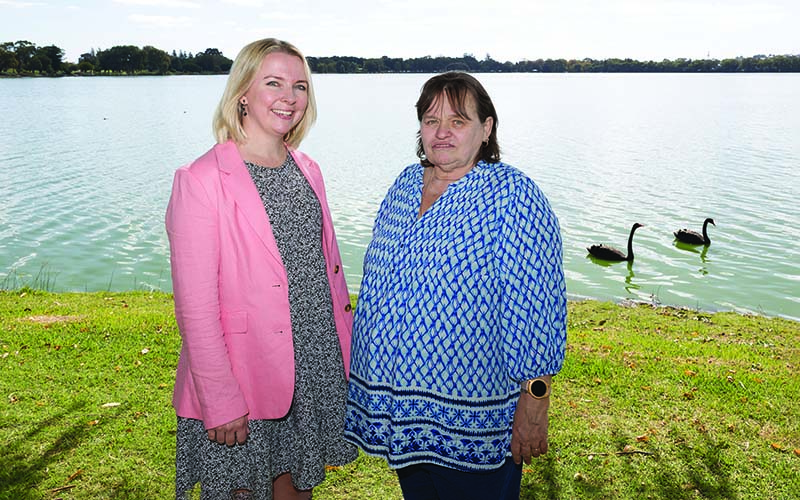

Tapping into the healing nature of water
In Aboriginal culture, water is life, holding powerful spiritual and cultural significance and acting as a vital source of connection, food and medicine.
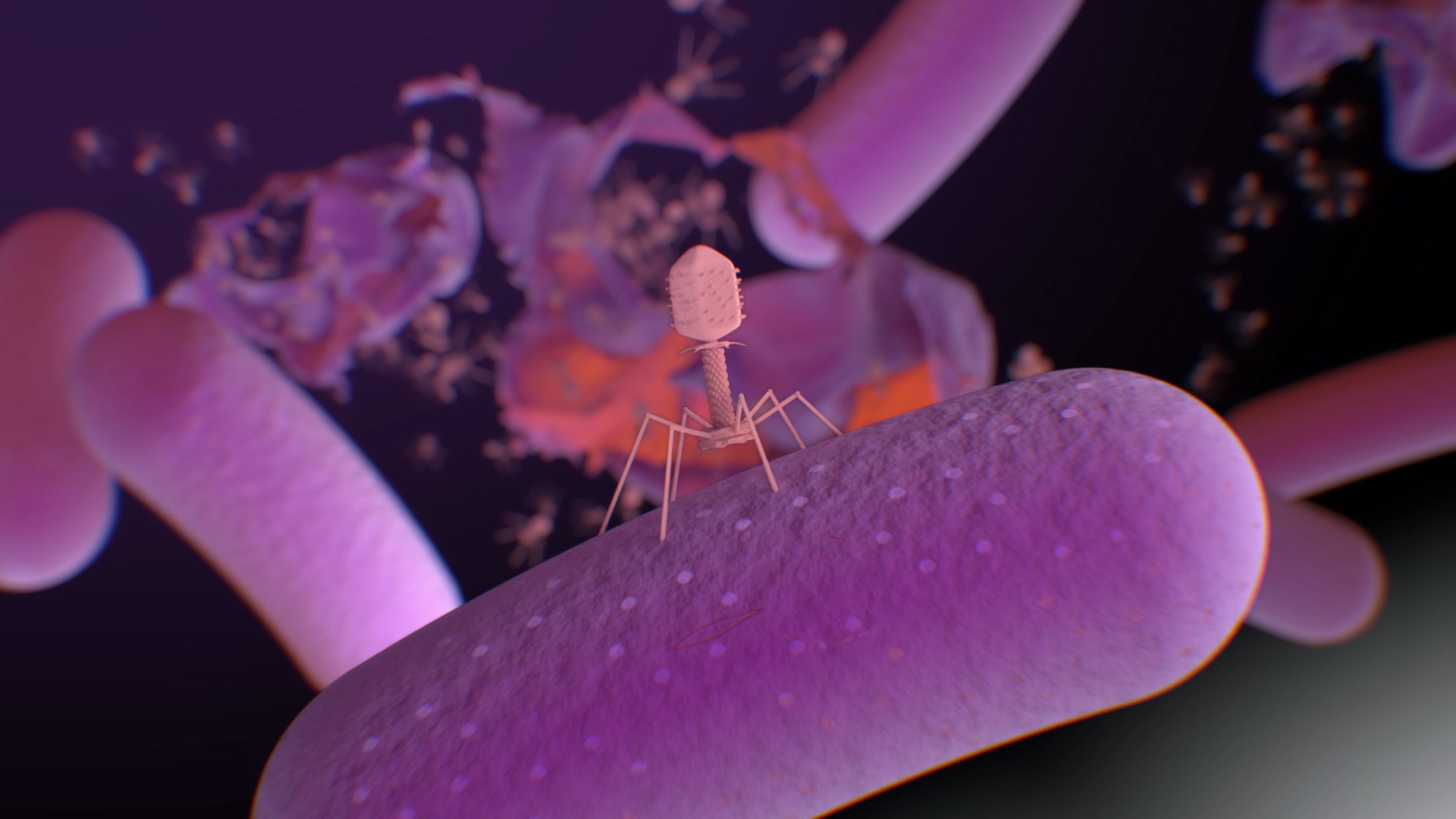
Phage WA
Leading the fight against Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) in Western Australia.
